责编 | 酶美



参考文献
Link, R. I. C. H. A. R. D., Daunt, D. A. V. I. D., Barsh, G. R. E. G., Chruscinski, A. N. D. R. Z. E. J., & Kobilka, B. R. I. A. N. (1992). Cloning of two mouse genes encoding alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtypes and identification of a single amino acid in the mouse alpha 2-C10 homolog responsible for an interspecies variation in antagonist binding. Molecular Pharmacology, 42(1), 16-27
Ruffolo Jr, R. R., Nichols, A. J., Stadel, J. M., & Hieble, J. P. (1993). Pharmacologic and therapeutic applications of alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 33(1), 243-279.
MacDonald, E., Kobilka, B. K., & Scheinin, M. (1997). Gene targeting—homing in on α2-adrenoceptor-subtype function. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 18(4), 211-219.
Wang, C. D., Buck, M. A., & Fraser, C. M. (1991). Site-directed mutagenesis of alpha 2A-adrenergic receptors: identification of amino acids involved in ligand binding and receptor activation by agonists. Molecular pharmacology, 40(2), 168-179.
Ramos, B. P., & Arnsten, A. F. (2007). Adrenergic pharmacology and cognition: focus on the prefrontal cortex. Pharmacology & therapeutics, 113(3), 523-536.
Maletic, V., Eramo, A., Gwin, K., Offord, S. J., & Duffy, R. A. (2017). The role of norepinephrine and its α-adrenergic receptors in the pathophysiology and treatment of major depressive disorder and schizophrenia: a systematic review. Frontiers in psychiatry, 8, 42.
Wade, S. M., Lim, W. K., Lan, K. L., Chung, D. A., Nanamori, M., & Neubig, R. R. (1999). Gi activator region of α2A-adrenergic receptors: distinct basic residues mediate Gi versus Gs activation. Molecular Pharmacology, 56(5), 1005-1013.
Eason, M. G., Kurose, H., Holt, B. D., Raymond, J. R., & Liggett, S. B. (1992). Simultaneous coupling of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors to two G-proteins with opposing effects. Subtype-selective coupling of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2 adrenergic receptors to Gi and Gs. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267(22), 15795-15801.
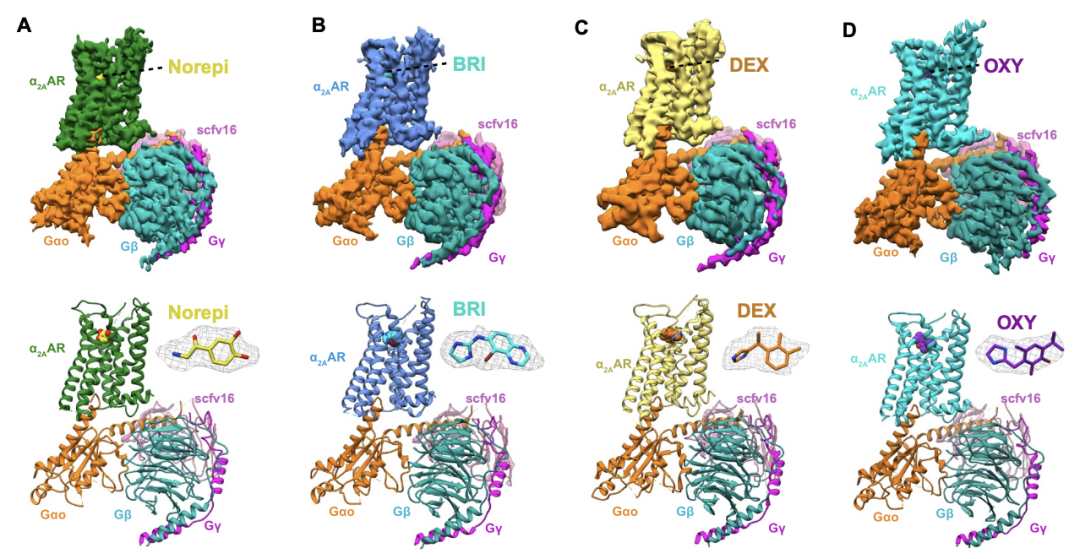
Qu, L., Zhou, Q., Xu, Y., Guo, Y., Chen, X., Yao, D., ... & Zhao, S. (2019). Structural basis of the diversity of adrenergic receptors. Cell reports, 29(10), 2929-2935.
Jasper, J. R., Lesnick, J. D., Chang, L. K., Yamanishi, S. S., Chang, T. K., Hsu, S. A., ... & Eglen, R. M. (1998). Ligand efficacy and potency at recombinant α2 adrenergic receptors: agonist-mediated [35S] GTPγS binding. Biochemical pharmacology, 55(7), 1035-1043.
Pao, C. S., & Benovic, J. L. (2005). Structure/Function Analysis of α2A-Adrenergic Receptor Interaction with G Protein-coupledReceptor Kinase 2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(12), 11052-11058.
DeGraff, J. L., Gurevich, V. V., & Benovic, J. L. (2002). The third intracellular loop of α2-adrenergic receptors determines subtype specificity of arrestin interaction. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(45), 43247-43252.
DeGraff, J. L., Gagnon, A. W., Benovic, J. L., & Orsini, M. J. (1999). Role of arrestins in endocytosis and signaling of α2-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(16), 11253-11259.
Giovannitti Jr, J. A., Thoms, S. M., & Crawford, J. J. (2015). Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists: a review of current clinical applications. Anesthesia progress, 62(1), 31-38.
Smith, H., & Elliott, J. (2001). Alpha2 receptors and agonists in pain management. Current opinion in Anesthesiology, 14(5), 513-518.
Rasmussen, S. G., Choi, H. J., Fung, J. J., Pardon, E., Casarosa, P., Chae, P. S., ... & Kobilka, B. K. (2011). Structure of a nanobody-stabilized active state of the β2 adrenoceptor. Nature, 469(7329), 175-180.
Rasmussen, S. G., DeVree, B. T., Zou, Y., Kruse, A. C., Chung, K. Y., Kobilka, T. S., ... & Kobilka, B. K. (2011). Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor–Gs protein complex. Nature, 477(7366), 549-555.
Xu, X., Kaindl, J., Clark, M. J., Hübner, H., Hirata, K., Sunahara, R. K., ... & Liu, X. (2021). Binding pathway determines norepinephrine selectivity for the human β1AR over β2AR. Cell Research, 31(5), 569-579.
Warne, T., Moukhametzianov, R., Baker, J. G., Nehmé, R., Edwards, P. C., Leslie, A. G., ... & Tate, C. G. (2011). The structural basis for agonist and partial agonist action on a β1-adrenergic receptor. Nature, 469(7329), 241-244.
Masureel, M., Zou, Y., Picard, L. P., van der Westhuizen, E., Mahoney, J. P., Rodrigues, J. P., ... & Kobilka, B. K. (2018). Structural insights into binding specificity, efficacy and bias of a β2AR partial agonist. Nature chemical biology, 14(11), 1059-1066.
Ring, A. M., Manglik, A., Kruse, A. C., Enos, M. D., Weis, W. I., Garcia, K. C., & Kobilka, B. K. (2013). Adrenaline-activated structure of β2-adrenoceptor stabilized by an engineered nanobody. Nature, 502(7472), 575-579.
Stanek, M., Picard, L. P., Schmidt, M. F., Kaindl, J. M., Hübner, H., Bouvier, M., ... & Gmeiner, P. (2019). Hybridization of β-adrenergic agonists and antagonists confers g protein bias. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 62(10), 5111-5131.
转载须知
【非原创文章】本文著作权归文章作者所有,欢迎个人转发分享,未经允许禁止转载,作者拥有所有法定权利,违者必究。




 个人中心
个人中心
 我是园区
我是园区